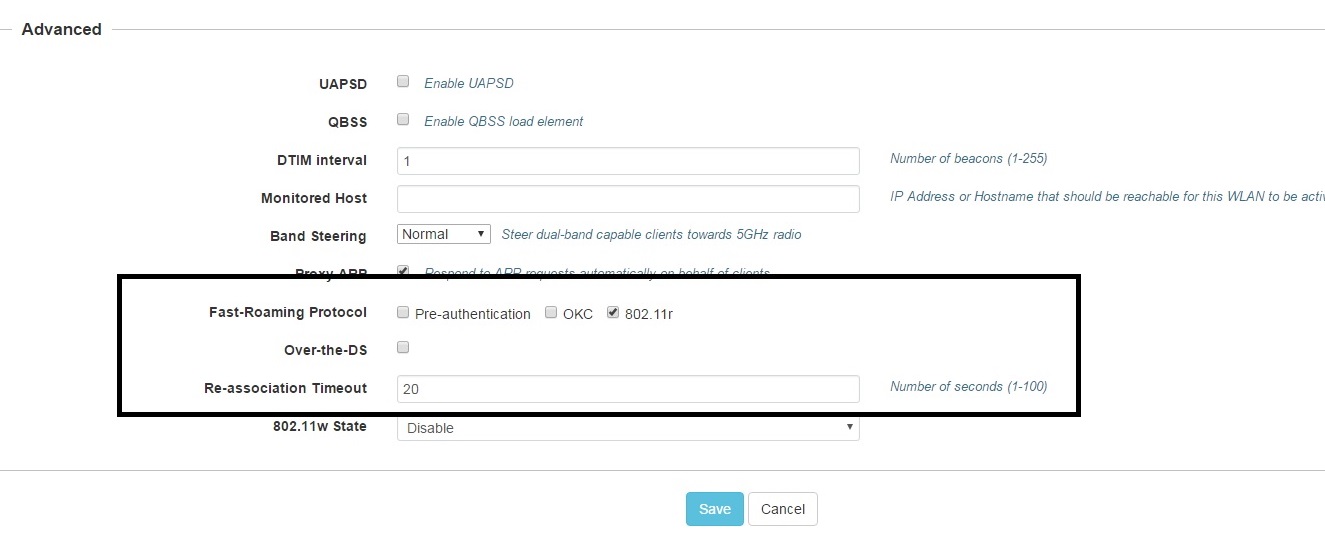
Fast roaming (802.11r) refers to the ability of a Wi-Fi-enabled device to quickly and seamlessly transition between different access points (APs) within a wireless network without experiencing significant disruptions in connectivity.
An example of where to enable the fast roaming protocol, 802.11r is illustrated above on the GNS-XV2-23T.
The traditional Wi-Fi roaming process involves a temporary disconnection from one access point and a subsequent reconnection to another, which can result in a brief interruption in service. Fast roaming aims to minimize this interruption, making the transition smoother and faster.
The need for fast roaming is particularly crucial in scenarios where continuous and uninterrupted connectivity is essential. Examples include applications like voice over IP (VoIP), video streaming, online gaming, and real-time data transmission. Fast roaming ensures that users can move freely within a Wi-Fi network without experiencing noticeable delays or drops in their network connection.
Several protocols and standards contribute to achieving fast roaming in Wi-Fi networks. One such standard is IEEE 802.11r, also known as Fast Basic Service Set (BSS) Transition. This standard introduces mechanisms to streamline the authentication and key negotiation processes during handovers between access points, reducing the time it takes for a device to switch from one AP to another.
Key techniques involved in fast roaming include:
-
Pre-authentication: Devices authenticate with a new access point before the actual handover, reducing the time needed to establish a connection when moving to a new coverage area.
-
Pairwise Master Key (PMK) Caching: Storing and reusing cryptographic keys associated with a user’s connection, allowing for faster reauthentication when switching between access points.
-
Fast Transition (FT): The FT protocol, defined in the IEEE 802.11r standard, facilitates fast roaming by enabling the secure and efficient transfer of authentication information during handovers.
-
Opportunistic Key Caching: This technique involves caching keys for potential future use, anticipating handovers and further reducing the authentication time.
Fast roaming enhances the user experience by minimizing disruptions during device mobility within a Wi-Fi network. It is especially beneficial in environments with high mobility, such as airports, train stations, retail spaces, and outdoor areas, as well as in applications involving devices like smartphones, tablets, laptops, and other wireless-enabled devices.